Biometric Authentication: Literature Review
Cyber-Physical Systems Applications and Features Literature Review
August 11, 2021Literature Review on the Glass Ceiling
August 11, 2021Biometric Authentication: Literature Review
BIOMETRIC AUTHENTICATION: LITERATURE REVIEW
INTRODUCTION
Human identification has generally been carried out by utilizing ID cards and passwords. Such techniques can be violated easily. Passwords can be guessed and ID cards can be robbed, rendering them temperamental [Jain et al. 2006].
< Jain, A., Bolle, R., & Pankanti, S. (Eds.). (2006). Biometrics: personal identification in networked society (Vol. 479). Springer Science & Business Media.>
Biometrics is defined as a process of identifying a person identity on the basis of physiological and behavioral features; it is capable of differentiating between the genuine person and the fake one. A biometric system is that system which identifies data of the person, by fetching the set of features and verifying it with the set stored in the database, which is dependent on the application context. An individual’s identity can be found out in two ways: Identification and verification. Working of biometric system is divided into eight stages (Liu and Silverman 2001). First, capturing the biometrics. Second, processing, enrolling and extraction of biometric template. Third, storing the data in tokens such as smart card. Fourth, lively scan the selected biometric. Fifth, processing of biometric and extraction of biometric template. Sixth, matching of biometric with the stored one. Seventh, matching score is being provided to the business application. Eighth, recording of correct audit train in regards to the system. Processing of biometric system is shown below:
< Liu, Simon, and Mark Silverman. “A practical guide to biometric security technology.” IT Professional 3.1 (2001): 27-32.>
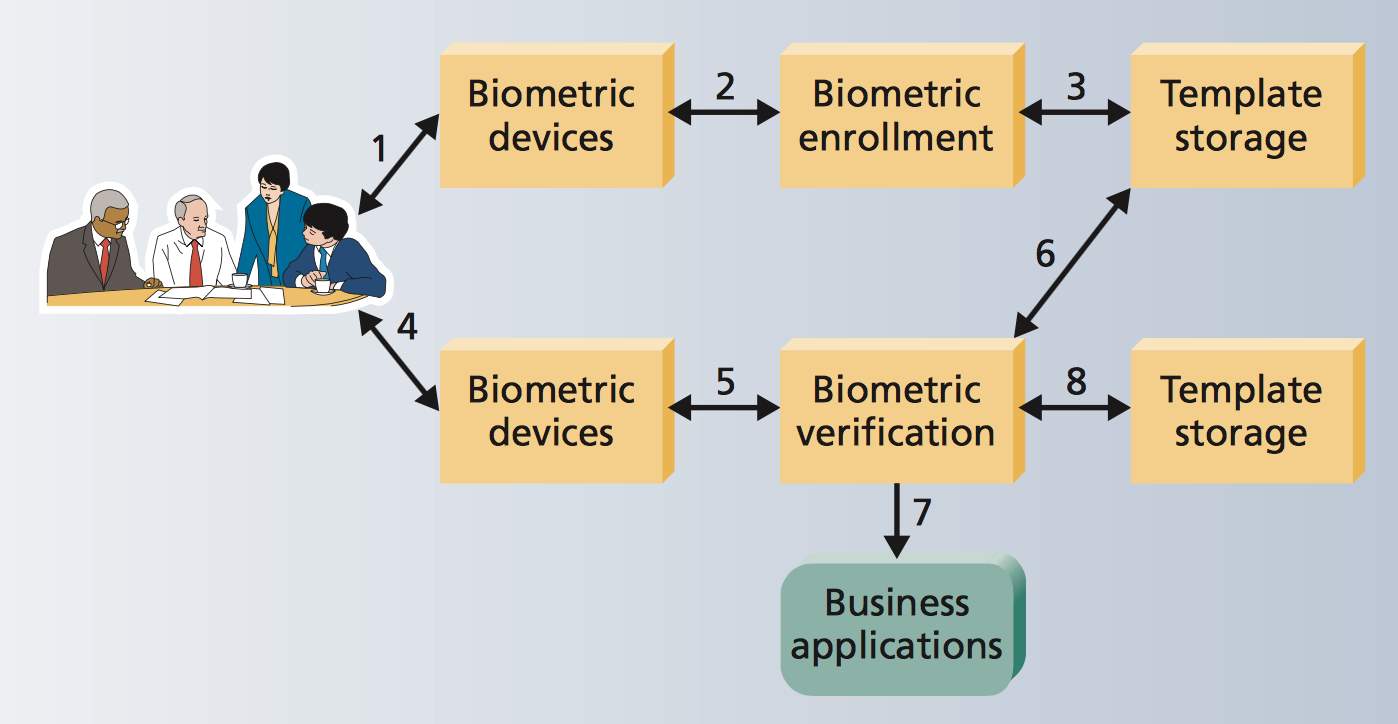
Figure 1How a biometric system work
MAIN MODULE:
BIOMETRIC SYSTEM
A biometric system is basically an example of acknowledgment framework that works by obtaining biometric information from an individual, processing the procured information, and comparing it against the layout set in the database. Based on the application setting, a biometric framework may work either in check mode or distinguishing proof model.
- In the mode of verification, the system approves an individual’s identity by comparing the captured biometric features with the individual’s biometric template stored in the framework database. In this system, a person who aims to be positively identified claims a factor – generally by means of an individual distinguishing proof number (PIN) or a user name – then the framework system conducts a one-to-one comparison to decide whether the claim is true or not. This mode aims to answer the question “is this person whom he/she claims to be”.
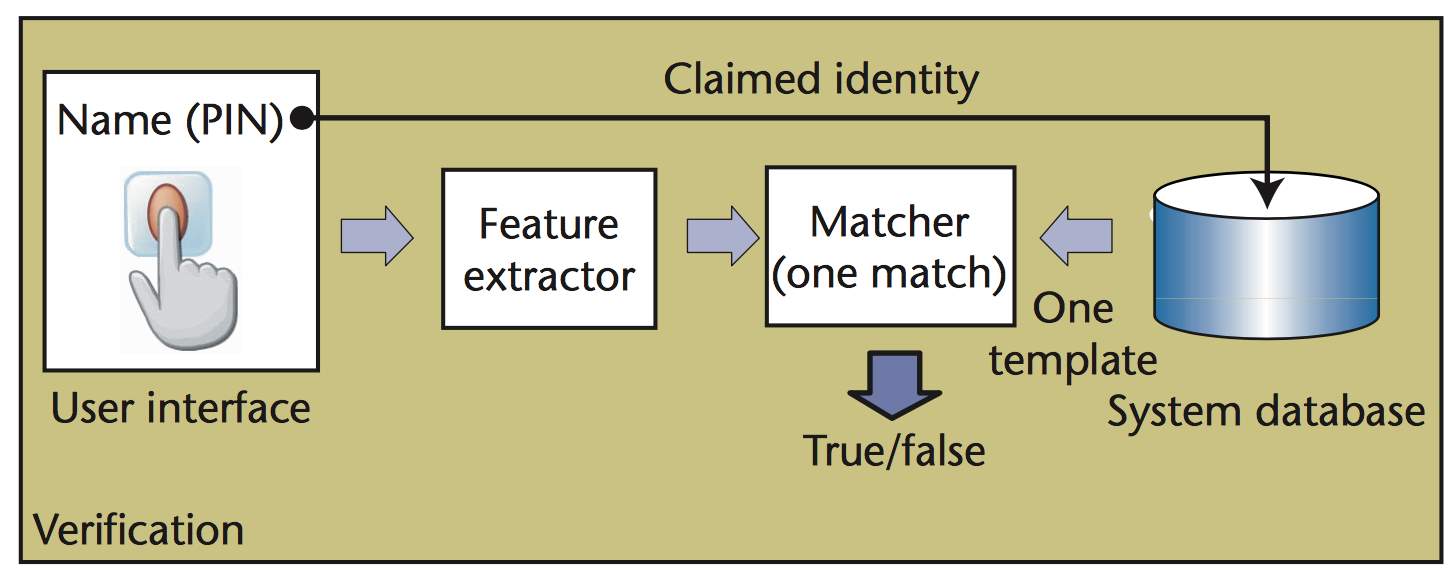
Figure 2 diagrams of verification task
- In the mode of identification, the individual’s identity is recognized by looking through template of all the users in the database for a match. Hence a system conducts a one -to- many comparisons to establish an individual’s identity. The identification mode classifies and identifies some unknown identity. It aims to answer questions such as “who is this person”. Distinguishing proof is a basic part in negative acknowledgment applications where the framework builds up whether the individual is who she denies being. The motivation behind negative acknowledgment is to keep an individual from utilizing numerous identities. Identification may also be utilized as a part of positive acknowledgment for convenience (where the induvial is not required to prove an identity). While the traditional methods of personal recognition such as passwords and tokens work for positive recognition, only biometrics can be used for negative recognition (SALIL, P., SHARATH, P, and ANIL, K. 2003).
< Prabhakar, Salil, Sharath Pankanti, and Anil K. Jain. “Biometric recognition: Security and privacy concerns.” IEEE security & privacy 99.2 (2003): 33-42.>
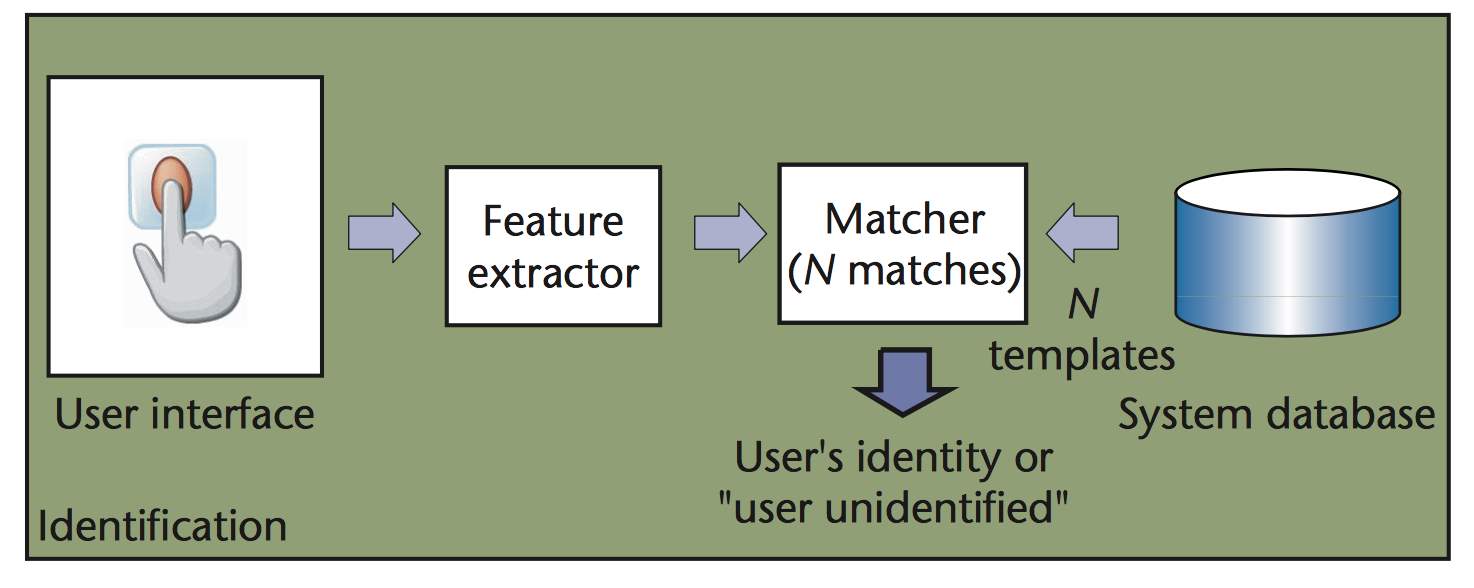
Figure 3 diagrams of Identification task
Physical biometric

